Data ingestion
Databricks supports multiple ingestion patterns for batch and streaming workloads.
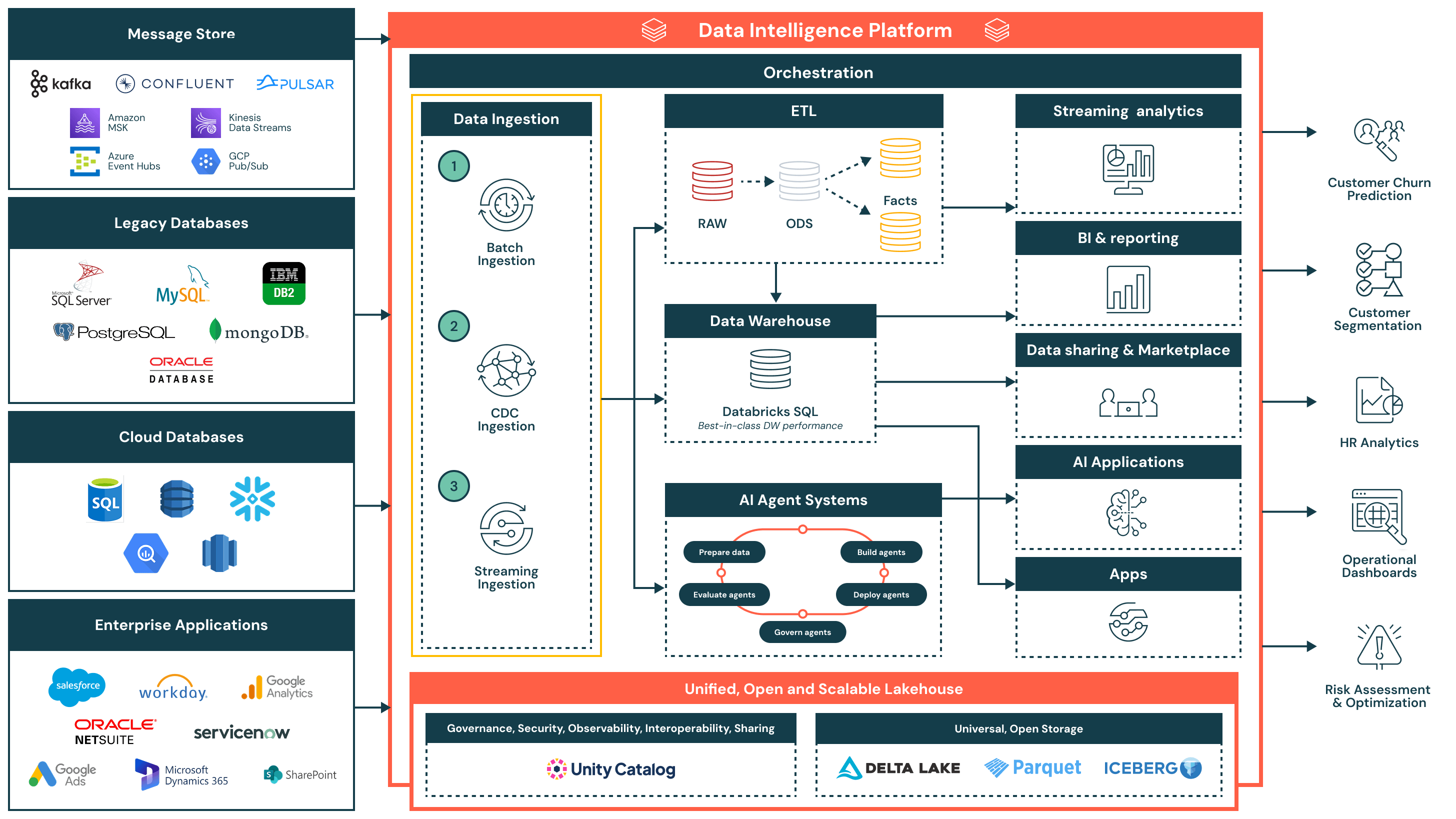
Partner integrations should follow these foundational practices:
- Use Unity Catalog volumes as the default governed landing/staging zone for file drops—this simplifies pathing and access control.
- Use Unity Catalog managed tables as targets. Managed tables are governed and optimized, delivering predictive optimization, automatic maintenance, lower cost, and faster performance. You may use external tables when required, but managed tables should be your default.
- Use Lakeflow Connect managed connectors to complement your integration as needed.
Documentation: Data Ingestion Reference Architecture | Batch ingestion and ETL | Streaming and CDC | Unity Catalog volumes | Managed tables | Lakeflow Connect
File-based ingestion
-
Incremental ingestion (process only new files since last run): Use Auto Loader within Lakeflow Spark Declarative Pipelines (SDP) for production-grade pipelines with autoscaling, schema evolution, and monitoring.
- SQL: Use Pipelines in Databricks SQL for the simplest declarative experience.
- Python: Use the Pipelines API for advanced transformations or external dependencies.
-
Non-incremental ingestion (one-time loads or full refresh):
- Small volumes (thousands of files): Use COPY INTO for simple, idempotent SQL-driven loading.
- Large volumes (millions of files): Use Auto Loader for efficient file discovery at scale.
Documentation: Auto Loader | Lakeflow SDP | Pipelines in Databricks SQL | COPY INTO | COPY INTO vs Auto Loader
Streaming and CDC
-
Bus-based streaming (Kafka, Kinesis, etc.): Use Spark Structured Streaming or SDP Flows to read from event queues. These maintain incremental state via checkpoints.
- SQL: Use Pipelines in Databricks SQL for the simplest declarative experience.
- Python: Use the Pipelines API for advanced transformations.
- Procedural: Use Structured Streaming APIs with Lakeflow Jobs.
-
Direct CDF-based CDC (no bus): Read the Change Data Feed and apply AUTO CDC in pipelines to handle ordering and SCD 1/2 automatically.
-
Snapshot-derived CDC (no bus): For sources that deliver periodic full snapshots, use AUTO CDC FROM SNAPSHOT (Python-only) to compute diffs and apply them declaratively.
-
Managed direct-write streaming (no bus): Use Zerobus to ingest streaming data directly into Databricks tables over a simple API, eliminating external message buses or staging.
-
Custom data source connectors: Use PySpark custom data sources for non-native systems (REST APIs, SaaS apps, proprietary sources). Use Lakeflow Community Connectors templates to accelerate development.
Documentation: Structured Streaming | SDP Flows | AUTO CDC | AUTO CDC FROM SNAPSHOT | Zerobus | Community Connectors
Other patterns
- Delta Sharing reads - Access shared datasets from other organizations
- External MCP servers - Connect AI agents to external data sources
- Lakehouse Federation - Query external catalogs without copying data
Documentation: Delta Sharing | External MCP servers | Lakehouse Federation
What's next
- Learn about data transformation patterns
- Explore serving and consumption options
- Review the integration requirements for foundational guidance